A Diamond's Value is based on Four Factors (C's)
In 1955, the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) introduced its Diamond Grading Report. Based on the 4Cs of diamond value and the International Diamond Grading System (both of which were created by the GIA in the 1940s), it single-handedly revolutionized the diamond industry. To this day, the Diamond Grading Report continues to provide in-depth analysis of the authenticity and quality of diamonds which fall into the D-to-Z color range.
The diamond industry grades and categorizes diamonds based on different characteristics. These are commonly known as the Four Cs of diamond value and are based upon:
- Cut
- Clarity
- Color
- Carat Weight
If you are hoping to purchase a diamond in the near future, it is important to understand these characteristics so that you can make the best choice as far as quality and price. A simple way to consider the 4Cs is to picture a seesaw. At one end is the size of the diamond (carat weight) and on the other end is the quality of the stone (the remaining Cs). If you are working within a certain price range, as the size increases the quality will diminish. Conversely, if the quality improves then the size will become smaller.
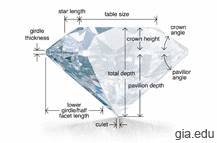
Diamond Cut
For the average person, the cut of a diamond is probably the most difficult factor to understand. It is also one of the most important. How a diamond is cut largely determines the brilliance and sparkle of the stone. These characteristics are some of the most cherished and sought-after features of a diamond.
Read more about Diamond Cut...
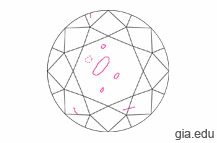
Diamond Clarity
Diamonds are formed by nature and usually contain inner flaws which are called inclusions. The number and size of these inclusions (and also how visible they are) determine the clarity of a diamond. A lack of inclusions and blemishes makes a diamond extremely rare and prohibitively expensive for most people.
Read more about Diamond Clarity...

Diamond Color
In the D-to-Z color range, a diamond's value is based on how nearly it approaches colorlessness. Less color equals higher value. Colorless diamonds allow the most refraction of light. This refraction produces a gem's sparkle. For this reason, colorless diamonds are usually the most desirable and also the most expensive. The more color a diamond has, the less light it can absorb.
Read more about Diamond Color...
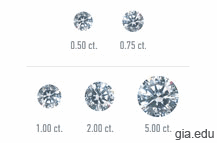
Diamond Carat Weight
All diamonds and gemstones are weighed in metric carats. One carat is equal to 0.2 grams. For comparison purposes, this is about the weight of a paperclip. Smaller diamonds are much more commonly found than larger ones. Because of this, the price of a diamond increases exponentially in relation to size.
Read more about Diamond Carat Weight...
